Services
Data Cabling
Data Cabling Refers to the Infrastructure that Supports the Transmission of Data
Data cabling refers to the infrastructure that supports the transmission of data between various network devices, such as computers, servers, routers, and switches. Specifically, it forms the backbone of modern IT and communication systems, thereby enabling reliable and efficient data transfer within and between organizations.
It is fundamental to building a robust and efficient network infrastructure, thereby enabling organizations to support their digital operations and communications effectively. Moreover, proper design, installation, and maintenance are crucial for ensuring the optimal performance and reliability of the network.
Types of Cables:
• Twisted Pair Cables: Commonly used for Ethernet networks. Categories include Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, and Cat7, each supporting different bandwidths and transmission speeds.
• Fiber Optic Cables: Utilized for high-speed and long-distance data transmission. Types include single-mode and multi-mode fibers, offering varying capacities and speeds.
Cable Structure:
• Conductors: Copper wires (twisted pairs) or glass/plastic fibers that carry data signals.
• Insulation: Material surrounding conductors to prevent signal interference and ensure data integrity.
• Sheath: Outer layer providing protection against physical damage and environmental factors.
Installation Considerations:
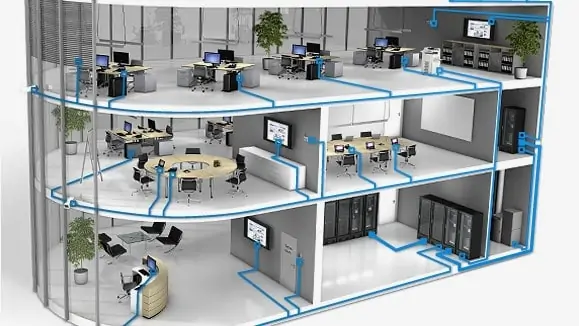
• Horizontal Cabling: Connects workstations and devices within a single floor or building.
• Vertical Cabling (Backbone): Links equipment rooms, telecommunications rooms (TRs), and different floors or buildings.
Termination and Connectivity:
• Patch Panels: Used to terminate and organize cables in equipment rooms or data centers.
• Jacks and Connectors: Provide interfaces for connecting cables to network devices (e.g., RJ45 connectors for Ethernet).
Performance and Standards:
• Compliance with standards such as those defined by the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) ensures reliability and interoperability.
• Standards specify parameters like maximum cable length, transmission speed, and performance requirements.
Benefits of Data Cabling:
Applications of Data Cabling:
Contact us today to discover how our expertise and dedication can benefit your telecommunications projects
Experience firsthand why Active Infrastructure Communications is the trusted choice for superior service and exceptional results.
